https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1D1iL824ssk

자신이 만든 패키지 아래에 model 패키지를 생성해 주고, Bank.kt 파일을 생성해 줍니다.
package com.study.hello_world.model
class Bank {
private var accountNumber: String
private val trust: Double
private val transactionFee: Int
constructor(accountNumber: String, trust: Double, transactionFee: Int){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
this.trust = trust
this.transactionFee = transactionFee
}
fun getAccountNumber(): String = accountNumber
fun setAccountNumber(accountNumber: String){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
}
}을 Bank.kt에 입력해 준 뒤
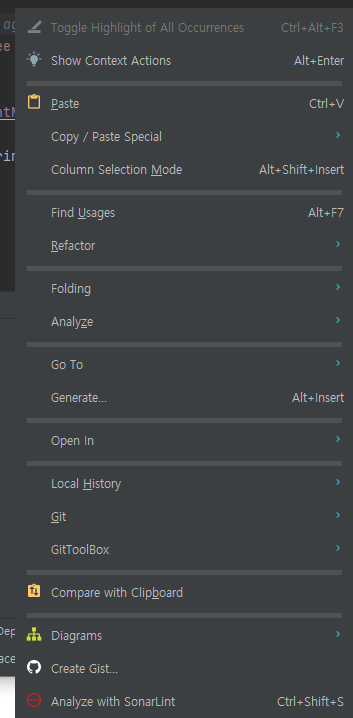
우클릭하면 해당 화면이 나오게 됩니다. Generate... 을 클릭해 줍니다. 혹은 Alt+Insert를 입력하셔도 됩니다.

해당 화면에서 equals() and hashCode()를 클릭해 줍니다. 다음을 눌러 전부 생성해 줍니다.
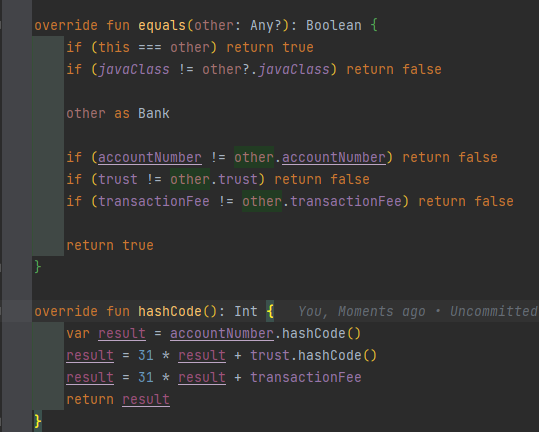
해당 함수가 추가된 뒤 다시 Gererate를 실행해 toString() 또한 추가해 줍니다.

해당 함수가 추가되게 됩니다.
package com.study.hello_world.model
class Bank {
private var accountNumber: String
private val trust: Double
private val transactionFee: Int
constructor(accountNumber: String, trust: Double, transactionFee: Int){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
this.trust = trust
this.transactionFee = transactionFee
}
fun getAccountNumber(): String = accountNumber
fun setAccountNumber(accountNumber: String){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
}
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (javaClass != other?.javaClass) return false
other as Bank
if (accountNumber != other.accountNumber) return false
if (trust != other.trust) return false
if (transactionFee != other.transactionFee) return false
return true
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
var result = accountNumber.hashCode()
result = 31 * result + trust.hashCode()
result = 31 * result + transactionFee
return result
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Bank(accountNumber='$accountNumber', trust=$trust, transactionFee=$transactionFee)"
}
}자바 형식의 코드 스타일이 완성되게 됩니다. 이를 코틀린 스타일로 변경해 보겠습니다.
val의 경우 final을 의미하며 setter로 값을 변경할 수 없습니다.
fun getAccountNumber(): String = accountNumber
fun setAccountNumber(accountNumber: String){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
}와 같은 코드는 코틀린에서는 사실 필요가 없습니다.
private var accountNumber: String
get() = field
set(value){ field = value }와 같이 default getter와 setter가 자동으로 생성됩니다.
var의 경우 get과 set이 생기며 val의 경우 get만 생기게 됩니다.
constructor(accountNumber: String, trust: Double, transactionFee: Int){
this.accountNumber = accountNumber
this.trust = trust
this.transactionFee = transactionFee
}기본 생성자 또한 필요가 없습니다.
class Bank(private val accountNumber: String
private val trust: Double
private val transactionFee: Int
)class 변수 들을 해당 괄호 안에 넣어주면 자동적으로 기본 생성자를 만들어 줍니다.
class Bank(
val accountNumber: String
val trust: Double
val transactionFee: Int
) {또한 내부에 선언하게 된다면 private가 기본 설정 값 이므로 만약 public으로 선언을 하고 싶으시다면
public val accountNumber: String과 같이 public을 붙여 주셔야 합니다.
data class Bank(
val accountNumber: String,
val trust: Double,
val transactionFee: Int
)와 같이 그냥 class가 아닌 data class로 생성하게 된다면
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (this === other) return true
if (javaClass != other?.javaClass) return false
other as Bank
if (accountNumber != other.accountNumber) return false
if (trust != other.trust) return false
if (transactionFee != other.transactionFee) return false
return true
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
var result = accountNumber.hashCode()
result = 31 * result + trust.hashCode()
result = 31 * result + transactionFee
return result
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Bank(accountNumber='$accountNumber', trust=$trust, transactionFee=$transactionFee)"
}내부의 equals와 hashcode, tostring또한 필요가 없어집니다.
data class 자체가 기본적으로 생성해주기 때문입니다.
package com.study.hello_world.model
data class Bank(
val accountNumber: String,
val trust: Double,
val transactionFee: Int
)최종적으로 해당코드가 기존의 코드와 똑같은 기능을 하게 됩니다.
'서버 > Kotlin-Spring_Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Kotlin-Spring_Boot 강의 정리) 6. Web Layer (0) | 2023.01.30 |
|---|---|
| Kotlin-Spring_Boot 강의 정리) 5. Service Layer (0) | 2023.01.29 |
| Kotlin-Spring_Boot 강의 정리) 4. Data Source (0) | 2023.01.28 |
| Kotlin-Spring_Boot 강의 정리) 2. Project Structure (0) | 2023.01.07 |
| Kotlin-Spring_Boot 강의 정리) 1. Hello World (0) | 2023.01.07 |




댓글